K hlavním faktorům ovlivňujícím životnost betonových konstrukcí patří přítomnost chloridů a vzdušného oxidu uhličitého, střídavé působení mrazu a mechanické namáhání konstrukce. V praxi lze jejich účinky zohlednit s využitím matematického modelování. V následujícím textu se autoři zaměřují na procesy prostupu chloridů a vzdušného CO2 (proces karbonatace) betonem a s tím související následnou korozi betonářské výztuže. Diskutován je rovněž vliv simultánního působení environmentálního a mechanického zatížení na životnost konstrukce.
Životnost (angl. service life) je časový (kvantitativní) údaj, který není materiálovou vlastností, ale je vztažen ke schopnosti materiálů, prvků a systémů zachovat specifické užitné i jiné vlastnosti na požadované úrovni za běžné údržby, během jistého časového rozpětí a za daných podmínek provozu a působení prostředí.
Stanovení zbytkové životnosti nových a stávajících konstrukcí, resp. způsoby stanovení životnosti dle TP 175 [1] jsou následující:
a) na základě znalosti životnosti podobné konstrukce (s podobnými vlastnostmi) umístěné v podobných podmínkách,
b) na základě urychlených zkoušek,
c) pomocí matematických modelů,
d) stochastickou metodou – lze využít metodu používající model spolehlivosti nebo metodu využívající kombinace statistických a deterministických modelů.
V případě stanovení životnosti dle a) se z důvodu velké variability zejména ve vlastnostech použitých materiálů a vlivem různorodého působení okolního prostředí jedná spíše o odhad. Pro stanovení dle b) je nutné, aby mechanismy degradace materiálu při urychlených zkouškách byly stejné jako v reálném prostředí. I při splnění této podmínky je při stanovení životnosti velkým problémem nedostatek dat ohledně míry degradace za normálních podmínek, které vychází z dlouhodobého monitorování stavu konstrukcí a dlouhodobých zkoušek. Jako vhodné se tedy jeví metody stanovení životnosti na základě matematického modelování a metoda stochastická (body c) a d) výše), kterým je věnována pozornost v tomto příspěvku.
Matematické modely degradačních procesů
Doba životnosti konstrukce tS je ve většině případů stanovena jako čas, který uplyne od uvedení konstrukce do provozu po okamžik, kdy je iniciován proces koroze výztuže, tedy tS = ti. V případě průniku chloridových iontů a vzdušného CO2 betonem je proces koroze započat difuzí chloridových iontů v betonu do hloubky, ve které se nachází ocelová výztuž, nebo karbonatací, která snižuje pH betonu při jeho styku s ocelovou výztuží. Při méně konzervativním pohledu lze dobu životnosti stanovit jako součet dvou časových úseků, tj. fáze iniciační ti a fáze propagační tp, tedy tS = ti + tp. Protože korozí výztuže dochází ke snižování její efektivní plochy, lze kritérium bezpečnosti definovat např. na základě dosažení limitní míry úbytku plochy výztužných vložek. Připomeňme zde, že zatímco se plocha výztuže snižuje, naopak vznikající korozivní produkty mají dvojnásobně až šestinásobně větší objem, což vede k nárůstu tahového napětí v okolním betonu, a tím vzniku podélných průběžných trhlin a následně i odlupování betonové krycí vrstvy.
Průběh koroze výztuže, která probíhá během propagačního stadia předpokládané životnosti konstrukce, tedy po dosažení iniciačního času depasivace výztuže, lze modelovat např. dle [2]. Zde jsou pro odhad průměru výztužného prutu d [mm] v čase použity vztahy:

kde di [mm] je počáteční průměr výztuže, icorr [μA/cm2] zohledňuje korozní proudovou hustotu (rychlost koroze) a Rcorr [-] typ koroze (rovnoměrná/důlková). Tentýž model je uveden v TP 175, kde je uvažováno s rovnoměrnou korozí (Rcorr = 2). Obdobně lze v čase stanovit hloubku důlku p [mm] při důlkové korozi jako [3]:
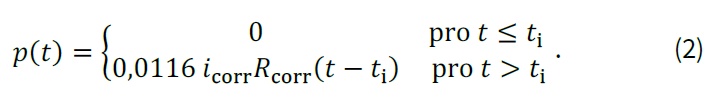
zbytkovou (čistou) plochu průřezu zkorodované tyče (Ar [mm2], šedá oblast na obrázku níže) v čase t > ti lze za předpokladu polokulovitého tvaru důlku spočítat jako [4]:
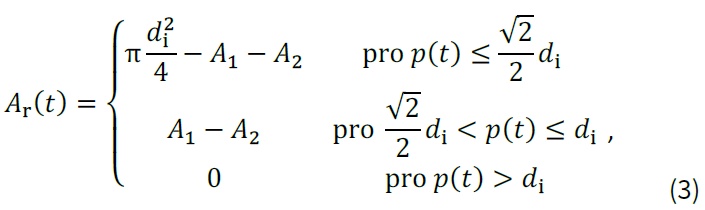
kde
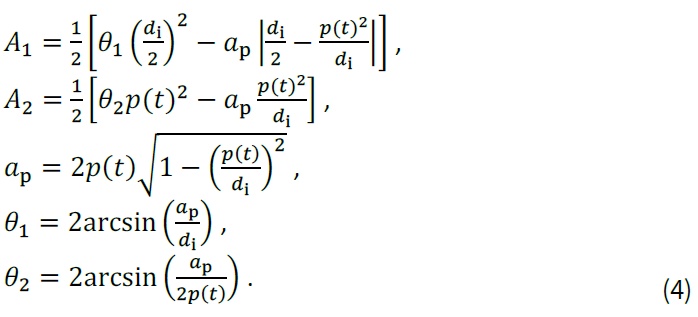
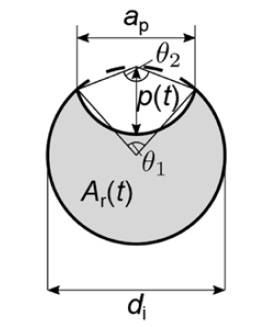
Plochu průřezu lze bez výrazné ztráty přesnosti spočítat s využitím jednodušší rovnice, která předpokládá kruhový tvar důlku a plochu výztuže spočtenou na základě překryvu dvou kružnic o poloměru di (obrázek níže), jako [5]:
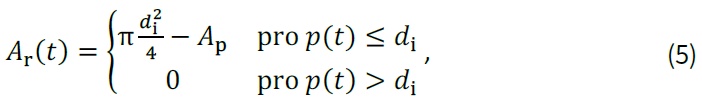
kde

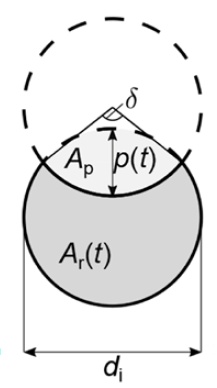
Jak již bylo uvedeno výše, depasivace výztuže může být způsobena zejména procesy karbonatace a/nebo působením chloridových iontů, kdy je iniciační čas stanoven na základě předpokladu, že karbonatační fronta dosáhne hloubky, ve které se nachází ocelové pruty, nebo hodnota koncentrace chloridových iontů v hloubce ocelových výztuží dosáhne kritické hodnoty. Matematické modely karbonatace a průniku chloridů vychází z II. Fickova zákona difuze:

kde C je koncentrace pronikající látky, x vzdálenost od povrchu, t čas difuze a D je obecně difuzní koeficient, který závisí na vlastnostech betonu a prostředí. Řešení této diferenciální rovnice se hledá pomocí Crankova postupu s využitím Gaussovy chybové funkce „erf(.)“.
Dle ISO 16204 [6] lze průběh karbonatační hloubky xc [mm] v čase t [roky] uvažovat dle:

kde parametr W [-] zohledňuje měnící se klimatické podmínky, jako jsou vlhkost a teplota, a k [-] je faktor popisující základní odolnost betonové směsi proti postupu karbonace. Při navrhování nových konstrukcí mohou být parametry W a k stanoveny s ohledem na data naměřená na podobných konstrukcích v podobných klimatických podmínkách, při ověřování stávajících konstrukcí je nutné je stanovit na základě měření. Pro modelování lze použít sofistikovaný model doporučovaný ve fib Bulletin 34 [7], kde je karbonatační hloubka stanovena na základě vztahu:
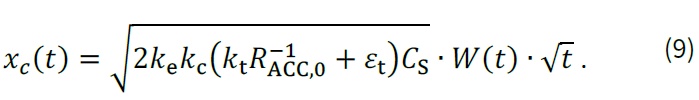
Parametr funkce prostřední ke zahrnuje vliv vlhkosti povrchu betonu (vliv relativní vlhkosti RH [%]) na hodnotu difuzního koeficientu, parametr kc zohledňuje vliv doby ošetřování čerstvé směsi (parametry tc [d] a bc [-]) na efektivní odpor betonu vůči karbonataci. Parametr R–1ACC,0 [(m2/s)/(kg/m3)] je inverzní efektivní odpor (rezistence) suché směsi vůči karbonataci, jehož hodnota je stanovena na základě testu betonových vzorků, které jsou vystaveny podmínkám, v nichž dochází k urychlení procesu karbonatace (tzv. ACC test). Parametry kt [-] a εt [(m2/s)/(kg/m3)] pokrývají rozdíly mezi vzorky testovanými ve zrychlených podmínkách a konstrukcí testovanou v podmínkách přírodních. Parametr CS zahrnuje vliv koncentrace CO2 v okolí a časově závislá funkce počasí W(t) [-] zohledňuje klimatické podmínky v důsledku deště (parametry pSR [-], tw [d] a bw [-]). Pro detailní doporučení týkající se jednotlivých parametrů modelu odkazujeme čtenáře na [7].
V případě působení chloridových iontů lze koncentraci chloridů C(x,t) [hm. % / cement] (vztaženo k hmotnosti cementu) v hloubce x [mm] (nejčastěji v hloubce betonové krycí vrstvy ocelové výztuže a) a čase t [roky] vyjádřit pro 1D případy jednoduchým analytickým vztahem:
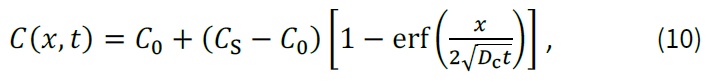
kde CS [hm. % / cement] je koncentrace chloridů na povrchu betonu, Dc [mm2/rok] je difuzní koeficient průniku chloridů betonem a C0 [mm2/rok] je počáteční koncentrace chloridů v betonu, při jejímž zanedbání (C0 = 0) je možné vztah (10) zjednodušit do formy (viz také TP 175 [1]):
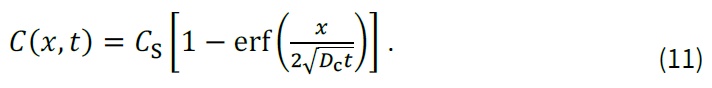
Řešení dle vztahů (10) a (11) platí za předpokladu homogenního materiálu plně nasyceného vodou a pro CS a Dc konstantní v čase. Díky své jednoduchosti je toto řešení využíváno již několik dekád a v různých modifikacích doporučováno rovněž řadou národních i mezinárodních normativních dokumentů.
Kritické body používání modelů průniků chloridů betonem jsou shrnuty v [8], kde je mj. zmíněna vysoká variabilita výsledků modelování vyvolaná často značnou nejistotou u hodnot modelových parametrů. Dalším hojně diskutovaným tématem je současné působení více degradačních procesů a časová závislost difuzního koeficientu a povrchové koncentrace chloridů.
Časovou závislost difuzního koeficientu Dc lze modelovat dle ISO 16204 funkcí [6]:
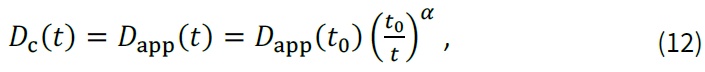
kde Dapp(t0) [mm2/rok] je skutečná hodnota difuzního součinitele stanovená v referenčním čase t0 [roky] (t0 = 28 dnů = 0,0767 let) a α [-] je faktor stárnutí betonu, který zohledňuje nárůst odolnosti betonu vůči pronikání agresivních látek vlivem jeho stárnutí (zrání), tzn. zohledňuje pokles hodnoty Dapp v čase díky hydrataci cementových složek (dochází ke změnám v pórové struktuře). Nutno podotknout, že jak při navrhování nových konstrukcí, tak při posuzování zbytkové životnosti stávajících konstrukcí by měl být faktor stárnutí α získán na základě pozorování konstrukcí in situ, kde je složení betonu, provedení a podmínky expozice agresivním látkám podobné podmínkám u skutečné konstrukce. Pro výpočet součinitele stárnutí jsou nutná pozorování během nejméně dvou období expozice (s dostatečným odstupem mezi pozorováními).
Model dle fib Bulletin 34 [7] zohledňuje časovou závislost difuzního koeficientu následovně:
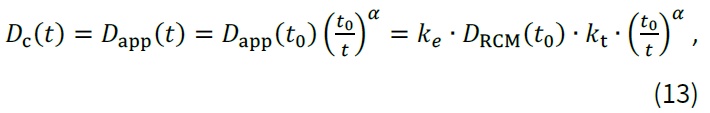
kde ke [-] je parametr prostředí zohledňující vliv teploty na hodnotu difuzního koeficientu (parametry T [°C] a be [°C]), DRCM(t0) [m2/s] je migrační koeficient chloridů, jehož hodnotu lze stanovit na základě zrychlené zkoušky migrace chloridů (RCM – rapid chloride migration test), a kt [-] je převodní součinitel jednotky difuzního koeficientu (kt = 3,1536∙106; 1 m2/s = 3,1536∙106 mm2/rok). Koncentrace chloridových iontů je pak stanovena na základě rovnice (10). S přihlédnutím k faktu, že při povrchu betonu vystaveného externímu působení chloridů obvykle vzniká vrstvička, kde difuze není hlavním procesem a proces penetrace chloridových iontů se odlišuje od II. Fickova zákona difuze z důvodu vystavení častému smáčení a následnému odpařování, tzv. konvekční zóna Δx, lze rovnici (10) dále modifikovat do tvaru [9]:
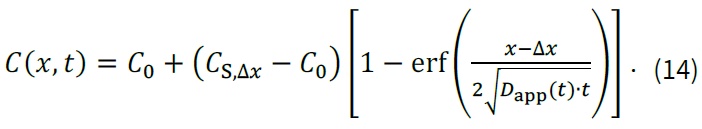
Maximální koncentrace chloridových iontů zde není na vnějším povrchu (x = 0), ale vzniká postupně v poloze x = ∆x, přičemž tato tloušťka je udávána v rozmezí 6 až 11 mm. V konvekční zóně se mohou koncentrace chloridů značně odchylovat od běžných hodnot, proto model dle (14) tyto hodnoty zanedbává a pracuje s tzv. náhradní koncentrací chloridů CS,Δx [hm. % / cement], která je aplikována až od hloubky větší, než je hloubka konvekční zóny. Takto upravený model má význam pouze pro dlouhé doby expozice, kdy se konvekční zóna vytvořila a zůstala po dlouhou dobu víceméně konstantní.
Pro vyjádření časové závislosti koncentrace chloridů na povrchu betonu CS lze využít lineární či odmocninové závislosti na čase s konstantou k dle [1], [10]:
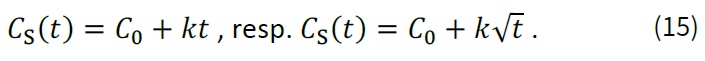
Poznamenejme zde, že funkce (15) nejsou jednoznačně vhodné pro popis působení chloridů z posypových solí, které je vázáno na střídání ročních období, působení deště (vyplachování solí z povrchu betonu) a příp. dalších klimatických či jiných vlivů (viz např. [11]). Toto tvrzení tak není v souladu s doporučeními TP 175, která naopak funkce (15) uvádí jako „nejvhodnější pro řešení případů, kdy do betonu pronikají chloridy z posypových solí“. Časová závislost CS vzhledem ke složitosti celé problematiky není rovněž zahrnuta v ISO 16204, a využití těchto modelů by tedy mělo být vždy důsledně zváženo s ohledem na možné chyby ve stanovení životnosti konstrukcí.
Intuitivně lze předpokládat, že procesy degradace budou probíhat rychleji u konstrukcí s trhlinami. Ani komise fib, ani komise ISO však nebyly schopny přijít s žádným obecným modelem, který by tento efekt zohledňoval, a bylo tedy dohodnuto zůstat u zjednodušeného přístupu, který předpokládá, že koroze výztuže není do určité šířky trhlin ovlivněna. V závislosti na stupni vlivu prostředí a citlivosti konstrukce je mezní šířka trhliny obvykle dána charakteristickou hodnotou (tj. 5% horní kvantil) v rozmezí 0,2 až 0,4 mm [12].
Dle zahraničních studií (uvedených např. v [13]) lze vliv napětí na rychlost karbonatace a průnik chloridů jednoduše zohlednit pomocí korekčních součinitelů. Hloubku karbonatace lze s ohledem na stav napětí prognózovat dle vztahu:

kde konstantu A je nutno vypočítat pomocí jakéhokoli vhodného modelu karbonatace v závislosti na složení a ošetřování betonu, typu cementu, vlhkosti prostředí, obsahu CO2, příp. na dalších parametrech (viz např. výše zmíněný model dle [7]). Opravný součinitel kσ [-] je definován zvlášť pro prvky namáhané tahem (napětí σt) a prvky namáhané tlakem (napětí σc) jako:
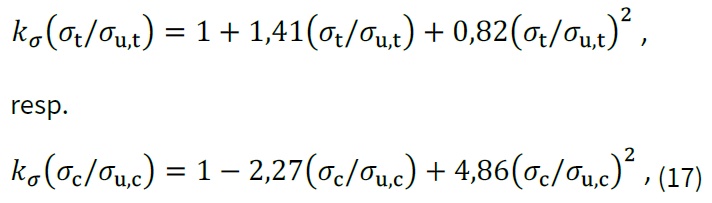
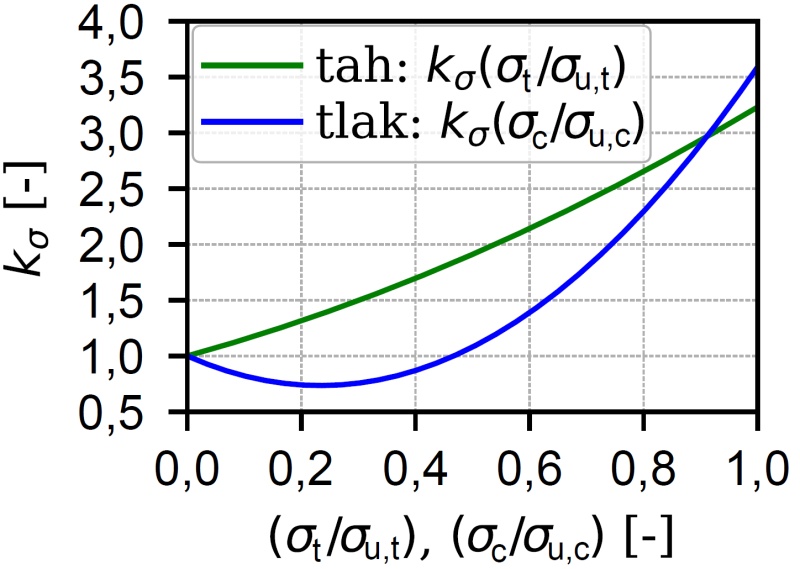
kde σu,t a σu,c reprezentují mezní napětí betonu v tahu a tlaku. Závislost součinitele kσ na poměru tahového/tlakového napětí a jeho mezní hodnoty jsou zobrazeny na obrázku níže. Je zřejmé, že malé tlakové zatížení (hodnoty (σc/σu,c) v rozsahu 0 až přibližně 0,5) snižuje rychlost průběhu karbonatace betonu, což je způsobeno částečným uzavíráním mikrotrhlin vlivem působícího tlakového napětí. Pokud však zatížení vzroste přibližně nad 50 % mezní tlakové únosnosti, uzavírání mikrotrhlin je kompenzováno vznikem nových trhlin, jimiž může vzdušný CO2 pronikat do betonu. Tím dochází k urychlení procesu karbonatace. S rostoucím tahovým zatížením pak dochází pouze k urychlení procesu karbonatace, neboť i vlivem nízkých hodnot tahového napětí dochází ke vzniku a otevírání mikrotrhlin, které slouží jako nové cesty pro penetraci CO2 do betonu.
Stejně jako v případě karbonatace lze o vliv mechanického zatížení na konstrukci rozšířit i modely působení chloridových iontů. S ohledem na trhlinky v betonu, vznikající působením napětí od zatížení, dochází k urychlení procesu difuze chloridových iontů. Při uvážení vlivu trhlin dochází ke změně hodnoty difuzního koeficientu (obecně označen D). Ten lze rozdělit do dvou částí, D0 [m2/s] a Dt [m2/s], jak je zobrazeno na obrázku níže. Difuzní koeficient D [m2/s] je stanoven s ohledem na šířku vzniklých trhlin w [mm] a jejich maximální vzdálenost sr,max [mm] jako [14]:
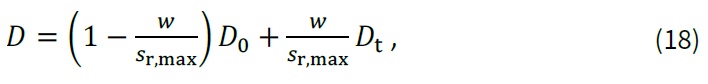
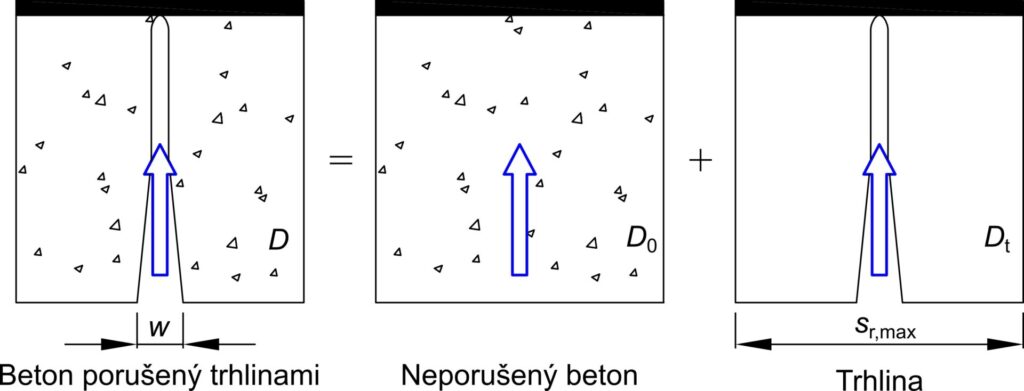
kde D0 je hodnota difuzního koeficientu pro neporušený beton a Dt hodnota difuzního koeficientu uvnitř trhliny, parametry w a sr,max lze získat např. měřením na reálné konstrukci nebo výpočtem dle [15]. Hodnoty Dt lze stanovit s ohledem na šířku trhliny následovně [16]:
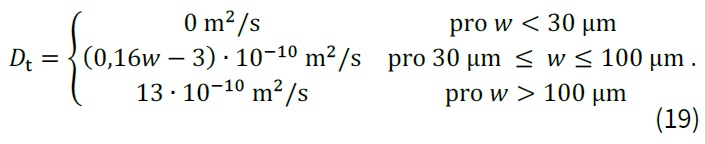
Aplikace uvedených vztahů pro modelování kombinovaného působení mechanického a environmentálního zatížení a ověření schopnosti těchto modelů dosahovat výsledků více se blížících realitě je uvedena v [17].
Studie
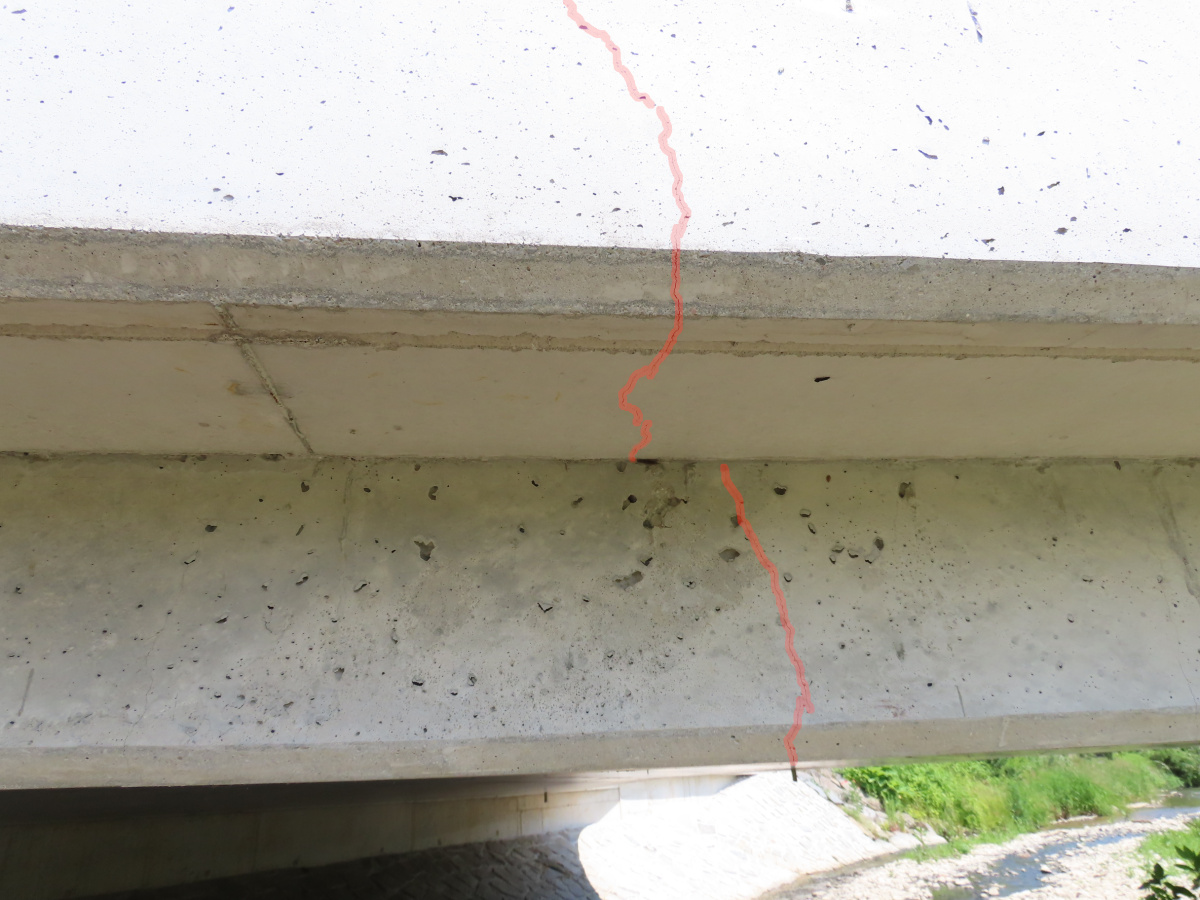
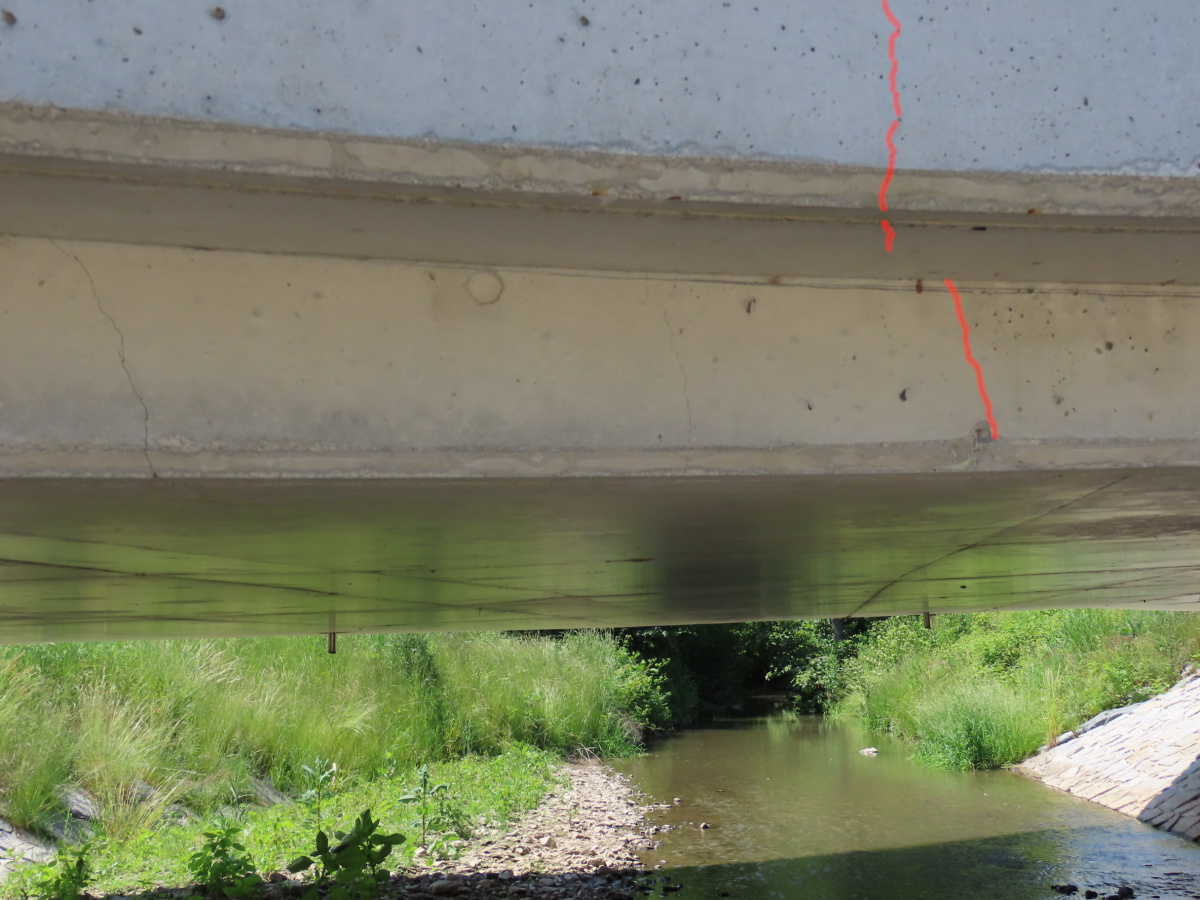
Pro studii stanovení zbytkové životnosti byla vybrána jednoduchá konstrukce železobetonového rámového mostu. Most byl uveden do provozu v roce 2019, po dvou letech jeho užívání byla uprostřed rozpětí rámové příčle zaznamenána souvislá trhlina šířky větší než 0,1 mm.
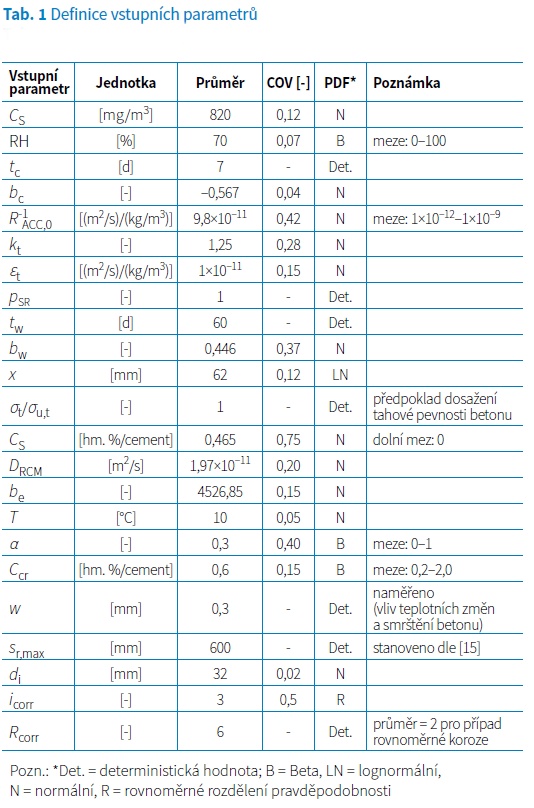
Životnost nosné konstrukce mostu byla stanovena s využitím matematického modelování degradačních procesů. Jako vstupní materiálové parametry byly uvažovány beton C30/37 (prostředí XD1 – prostředí středně mokré, vlhké a povrch betonu vystavený chloridům rozptýleným ve vzduchu; vodní součinitel w/c = 0,55), výztuž B500B,A profilu 32 mm, krycí vrstva 50 mm, 12 mm třmínky (tzn. krytí hlavní výztuže a = 62 mm). Pro modelování degradačních procesů byly využity výše zmíněné modely dle fib Bulletin 34 [7] a TP 175 [1], přičemž vstupní parametry byly definovány dle tab. 1. Poznamenejme zde, že pro stanovení zbytkové životnosti byla využita kombinace deterministických a stochastických modelů, kde deterministické hodnoty karbonatační hloubky, koncentrace chloridů a úbytku výztužné plochy v čase byly stanoveny na základě středních hodnot vstupních parametrů (sloupec Průměr v tab. 1). Pro zohlednění variability ve vlastnostech materiálů a charakteristikách působícího okolního prostředí byly tytéž veličiny stanoveny s využitím stochastického modelování na základě vhodně zvoleného statistického modelu vstupních veličin (sloupce COV a PDF v tab. 1, které značí variační koeficient, resp. funkci rozdělení pravděpodobnosti).
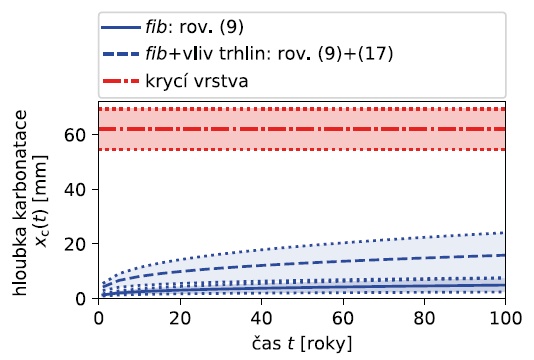
Výsledky jsou zřejmé z obrázků níže, kde jsou zobrazeny střední hodnoty (deterministický model) ± směrodatné odchylky (stochastický model) karbonatační hloubky, koncentrace chloridů a úbytku výztužné plochy v čase. Pro stochastické modelování byl využit software FReET‑D (viz např. [18]), statistické veličiny byly stanoveny na základě stovky náhodných simulací.
Při deterministickém výpočtu se nepředpokládá dosažení depasivace výztuže vlivem karbonatace ani působením chloridů po celou dobu návrhové životnosti konstrukce. Z výsledků stochastického modelování pak plyne určitá variabilita výsledků modelování – např. lze dle TP 175 očekávat brzkou depasivaci vlivem působení chloridových iontů (zelená barva na druhém obrázku). Zde poznamenejme, že model dle TP 175 je v této věci na straně bezpečné, neboť neuvažuje nárůst odolnosti betonu vůči pronikání agresivních látek vlivem jeho stárnutí. Při uvažování modelu dle fib není v hloubce betonové krycí vrstvy dosaženo kritické hodnoty koncentrace chloridových iontů ani při zohlednění variability vstupních veličin (modrá barva na druhém obrázku), a je tedy zřejmé, že z hlediska mezního stavu trvanlivosti je návrh konstrukce s ohledem na dostatečnou krycí vrstvu zcela v pořádku.
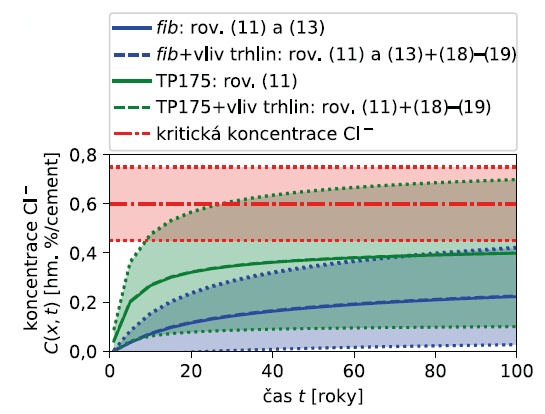
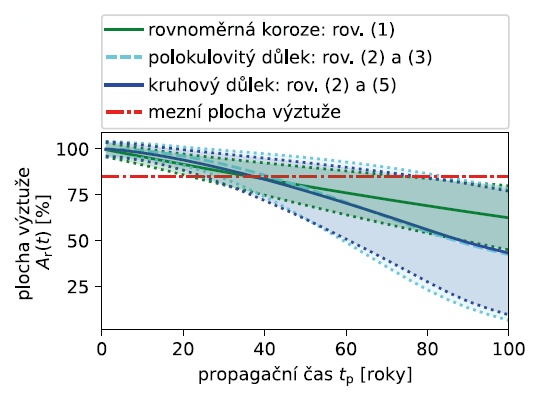
V případě stanovení zbytkové životnosti konstrukce méně konzervativně (jako součet iniciačního a propagačního času) by kritérium bezpečnosti, definované dle ČSN 73 6221 [19] pro velmi špatný (VI), až havarijní stav (VII) dosažením mezní hodnoty zkorodované plochy výztuže na úrovni 15 %, bylo dosaženo přibližně po 40 letech probíhající koroze výztuže (obrázek níže). Teoretické matematické modely stanovují, že za předpokladu normálního rozdělení průřezové plochy výztuže bude korozivního úbytku ve výši 15 % v čase 40 let (počítáno od započetí procesu koroze) dosaženo s pravděpodobností 47,6 až 56,4 % (dle vztahu, na jehož základě je počítána zbytková plocha zkorodované výztuže Ar). V případě, kdy nebudou přijata dodatečná opatření ve vztahu ke zjištěné závadě v podobě lokalizované trhliny, bude konstrukce po 40 letech užívání s touto pravděpodobností zařazena do stupně stavebního stavu VI, až VII a bude třeba přijmout omezující opatření v rámci jejího užívání, v krajním případě dojde k jejímu uzavření. Poznamenejme zde, že při zjištění korozivního úbytku/oslabení průřezové plochy výztuže do 1 % je ve vztahu k zařazení konstrukce do stavebního stavu IV (uspokojivý) doporučeno provést přepočet zatížitelnosti. Takového úbytku výztužné plochy je na základě matematického modelování dosaženo s 50% pravděpodobností za 2 roky až 11 let od započetí procesu koroze.
Závěr
V případě, kdy je správce stavebního objektu nebo stavební inženýr postaven před nutnost stanovit zbytkovou životnost betonových konstrukcí ve vztahu k probíhajícím degradačním procesům betonu, korozi výztuže a aktuálnímu stavebně-technickému stavu, jeví se využití vhodných matematických modelů v kombinaci se stochastickými metodami jako velmi rychlý a efektivní nástroj oproti postupům hodnocení zbytkové životnosti na základě znalosti životnosti podobné konstrukce umístěné v podobných podmínkách nebo na základě urychlených zkoušek. Využití pokročilých metod stochastické analýzy životnosti umožňuje ve větší míře získat představu o průběhu probíhajících degradačních procesů s možností provést časovou predikci poškození konstrukce v čase a stanovit hodnoty teoretické pravděpodobnosti poruchy při překročení limitních hodnot, jako je např. korozivní oslabení betonářské výztuže.
Závěrem poznamenejme, že matematické a stochastické modely degradace betonu a koroze výztuže vyžadují znalost vstupních parametrů a jejich pravděpodobnostních modelů, což se v některých případech může jevit jako nevýhoda. Matematické modely je ovšem možné kalibrovat na základě výsledků provedených reálných měření in situ a na základě provedených diagnostických průzkumů. Vhodné funkce rozdělení pravděpodobnosti a statistické charakteristiky je možné získat i v dostupné literatuře a některých normativních dokumentech.
Příspěvek vznikl za podpory prostředků Grantové agentury České republiky v rámci projektu č. 22 – 00774S.
Literatura:
[1] TP 175. Stanovení životnosti betonových konstrukcí objektů pozemních komunikací. Praha: Ministerstvo dopravy, Odbor pozemních komunikací, 2006.
[2] ANDRADE, C., SARRIA, J., ALONSO, C. Corrosion rate field monitoring of post-tensioned tendons in contact with chlorides. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Durability of Building Materials and Components, s. 959 – 967. Stockohlm, 1996.
[3] GONZÁLEZ, J., ANDRADE, C., ALONSO, C., FELIU, S. Comparison of rates of general corrosion and maximum pitting penetration on concrete embedded steel reinforcement. Cement and Concrete Research. 1995, Vol. 25, No. 2, s. 257 – 264.
[4] VAL, D. V., STEWART, M. G., MELCHERS, R. E. Effect of reinforcement corrosion on reliability of highway bridges. Engineering Structures. 1998, Vol. 20, No. 11, s. 1010 – 1019.
[5] KAGERMANOV, A., MARKOVIC, I. An overview on finite element-modelling techniques for structural capacity assessment of corroded reinforced concrete structures. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering. 2022.
[6] ISO 16204. Durability – Service Life Design of Concrete Structures. Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 2012.
[7] fib Bulletin No. 34 Model Code for Service Life Design. Lausanne, Switzerland: International Federation for Structural Concrete (fib), 2006.
[8] TEPLÝ, B. Působení chloridů na beton: Souvislosti, důsledky, modelování, testování, současný stav poznání. Beton TKS. 2018, roč. 18, č. 6, s. 62 – 65.
[9] GEHLEN, CH. Probabilistische Lebensdauerbemessung Stahlbetonbauwerken, Zuverlässigkeitsbetrachtungen zur wirksamen Vermeidung von Bewehrungskorrosion. Heft 510 der Schriftenreihe des DAfStb. Berlin: Beuth Verlag, 2000.
[10] PETCHERDCHOO, A. Time dependent models of apparent diffusion coefficient and surface chloride for chloride transport in fly ash concrete. Construction and Building Materials. 2013, Vol. 38, s. 497 – 507.
[11] TEPLÝ, B., VOŘECHOVSKÁ, D., KONEČNÝ, P., ŠOMODÍKOVÁ, M. Otázky modelování průniku chloridů betonem. Beton TKS. 2017, roč. 17, č. 2, s. 9 – 13.
[12] HELLAND, S. Design for service life: implementation of fib Model Code 2010 rules in the operational code ISO 16204. Structural Concrete. 2013, Vol. 14, No. 1, s. 10 – 18.
[13] RILEM. Publications on Durability of Reinforced Concrete Structures under Combined Mechanical Loads and Environmental Actions: An Annotated Bibliography. In: YAO, Y., WANG, L., WITTMANN, F. H. Report rep043. 2013.
[14] ZHANG, X., ZHAO, Y., XING, F., LU, Z. Coupling effects of influence factors on probability of corrosion initiation time of reinforced concrete. Journal of Central South University of Technology. 2011, Vol. 18, No. 1, s. 223 – 229.
[15] ČSN EN 1992 – 1‑1. Eurokód 2: Navrhování betonových konstrukcí – Část 1 – 1: Obecná pravidla a pravidla pro pozemní stavby. Praha: ČNI, 2006.
[16] DJERBI, A., BONNET, S., KHELIDJ, A., BAROUGHEL-BOUNY, V. Influence of transversing crack on chloride diffusion into concrete. Cement and Concrete Research. 2008, Vol. 38, No. 6, s. 877 – 883.
[17] TEPLÝ, B., VOŘECHOVSKÁ, D., ŠOMODÍKOVÁ, M., LEHKÝ, D. Modelování životnosti a spolehlivosti betonových konstrukcí při kombinaci mechanického a environmentálního zatížení. Beton TKS. 2016, roč. 16, č. 2, s. 37 – 39.
[18] TEPLÝ, B., NOVÁK, D. Predikce degradace betonových konstrukcí výpočetním modelováním. Beton TKS. 2014, roč. 14, č. 2, s. 58 – 59.
[19] ČSN 73 6221. Prohlídky mostů pozemních komunikací. Praha: ÚNMZ, 2018.




